A. Berdasarkan Waktu (Present, Past, Future)
1. Present
A. SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE
Simple present tense digunakan untuk menyatakan fakta, kebiasaan, dan kejadian yang terjadi pada saat sekarang ini.
Simple present tense dibentuk dari verb-1 (present tense) atau linking verb “be” (is, am, are). Apa itu verb-1? Verb-1 merupakan bare infinitive dengan tambahan -s atau -es (contoh verb-1: does, goes, wants) khusus untuk subject berupa singular noun (kata benda tunggal: Dina, table, book) atau third person singular pronoun (kata ganti orang ketiga tunggal: she, he, it); atau tanpa tambahan apapun (contoh verb-1: do, go, want) untuk subject berupa plural noun (boys, men, books) atau plural pronoun (we, they), pronoun I/you, atau compound subject (you and me, Yudi and Nabila)
(+) S + V1/Vs/es
I play badminton everyday.
She plays badminton everyday.
I don’t play badminton everyday.
She doesn’t play badminton everyday.
(?) Do/does + S + V1?
Do I play badminton everyday?
Does she play badminton everyday?
Pada kalimat positif, normalnya auxiliary verb (do/does) tidak digunakan, melainkan hanya digunakan jika perlu untuk memberi penekanan pada keharusan melakukan aksi.
Secara singkat perhatikan pada tabel berikut:

Present continuous tense digunakan untuk membicarakan aksi yang sedang berlangsung sekarang atau rencana dimasa depan
(+) S + be (is, am, are) + V–ing
I am repairing your bicycle now.
He is repairing your bicycle now.
They are repairing your bicycle now
(─) S + be (is, am, are) + not V–ing
I am not repairing your bicycle now.
They aren’t repairing your bicycle now
(? ) Be (is, am, are) + S + V–ing?
Am I repairing your bicycle now?
Is he repairing your bicycle now?
Are they repairing your bicycle now?
Secara singkat perhatikan pada tabel berikut:

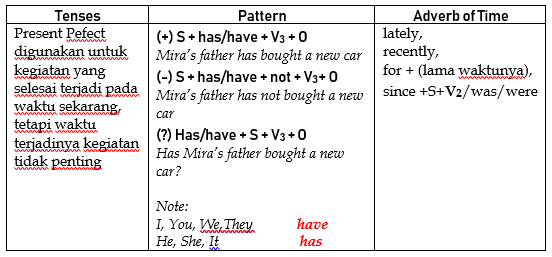
Present perfect tense digunakan untuk mengungkapkan suatu aktivitas atau situasi yang telah dimulai di masa lalu dan telah selesai pada suatu titik waktu tertentu di masa lalu atau masih berlanjut sampai sekarang.
(+) S + has/have + V3
I have opened the door since 7 o’clock.
He has opened the door since 7 o’clock.
(─) S + has/have not + V3
I have not opened the door.
She has not opened the door.
(?) Has/have +S + V3?
Have you opened the door?
Has she opened the door?
Secara singkat perhatikan pada tabel berikut:
Present perfect continuous tense digunakan untuk mengungkapkan aksi yang telah selesai pada suatu titik dimasa lampau atau aksi telah dimulai di masa lalu dan terus berlanjut sampai sekarang. Biasanya aksi tersebut ada durasi waktu tertentu dan ada relevansinya dengan kondisi sekarang.
(+) S + has/have + been + V-ing
They have been waiting for two hours.
He has been waiting for two hours.
(─) S + has/have not + been + V-ing
They have not been waiting for two hours.
He has not been waiting for two hours.
(?) Has/have + S + been + V-ing?
Have they been waiting for two hours?
Has he been waiting for two hours?
E. SIMPLE PAST TENSE
Simple past tense digunakan untuk menunjukkan bahwa suatu kejadian terjadi di masa lampau.
(+) S + V2
She bought the bicycle yesterday.
(─) S + did not + V1
She did not buy the bicycle yesterday.
(? ) Did + S + V1?
Did she buy the bicycle yesterday?
F. PAST CONTINUOUS TENSE
Past continuous tense digunakan untuk mengungkapkan bahwa suatu aksi sedang terjadi pada waktu tertentu di masa lampau.
(+) S + be (was, were) + V-ing
He was reading a book when I came.
They were reading a book when I came.
(─) S + be (was, were) not + V-ing
He was not reading a book when I came.
They were not reading a book when I came
(? ) Be (was,were) + S + V-ing?
Was he reading a book when I came?
Were they reading a book when I came?
G. PAST PERFECT TENSE
Past perfect tense digunakan untuk menyatakan bahwa suatu aksi telah selesai pada suatu titik di masa lalu sebelum aksi lainnya terjadi.
(+) S + had + V3
He had eaten the food before his mother arrived.
(─) S + had not + V3
He had not eaten the food before his mother arrived.
(? ) Had + S + V3?
Had he eaten the food before his mother arrived?
H. PAST PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE
Past perfect continuous tense digunakan untuk mengungkapkan suatu aksi (dengan durasi waktu tertentu) telah selesai pada suatu titik waktu tertentu dimasa lalu.
(+) S + had + been + V-ing
I had been living in Japan for 2 years before I moved to Italy.
(─) S + had not + been + V-ing
I had not been living in London for 2 years before I moved to Italy.
(? ) Had + S + been + V-ing?
Had you been living in London for 2 years before I moved to Italy?
I. SIMPLE FUTURE TENSE
Simple future tense digunakan untuk menyatakan bahwa suatu aksi terjadi dimasa depan, secara spontan atau terencana.
Tense ini juga dapat digunakan untuk membentuk conditional sentence tipe 1.
Simple future tense dibentuk dari modal “will” atau “shall” dan bare infinitive (bentuk dasar verb) atau dibentuk dari phrasal modal “be going to” dan bare infinitive (base form verb).
(+) S + will/shall +V1
She will borrow the book tomorrow.
(─) S + will/shall not + V1
She will not borrow the book tomorrow.
(?) Will/shall + S + V1?
Will she borrow the book tomorrow?
J. FUTURE CONTINUOUS TENSE
Future continuous tense digunakan untuk mengungkapkan aksi yang akan sedang terjadi pada waktu tertentu di masa depan.
(+) S + will/shall + be + V-ing
I will be coming there next week.
(─) S + will/shall not + be V-ing
I will not be coming there next week.
(? ) Will/shall + S + be + V-ing?
Will you be coming there next week?
K. FUTURE PERFECT TENSE
Future perfect tense digunakan untuk mengungkapkan bahwa suatu aktivitas akan sudah selesai pada suatu titik waktu di masa depan.
(+) S + will/shall +have + V3
He will have finished this assignment by the end of this week.
(─) S + will/shall not + have + V3
He will have not finished this assignment by the end of this week.
(?) Will/shall + S + have + V3?
Will he have finished this assignment by the end of this week?
L. FUTURE PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE
Future perfect continuous tense digunakan untuk mengungkapkan bahwa suatu aksi akan sudah berlangsung selama sekian lama pada titik waktu tertentu di masa depan.
(+) S + will/shall +have + been + V-ing
He will have been sleeping for 2 hours before she arrives.
(─) S + will/shall not + have + been + V-ing
He will not have been sleeping for 2 hours before she arrives.
(?) Will/shall + S + have + been + V-ing?
Will he have been sleeping for 2 hours before she arrives?
M. SIMPLE PAST FUTURE TENSE
Simple past future tense digunakan untuk menyatakan suatu aksi yang akan dilakukan, membuat prediksi, dan membuat janji di masa depan pada saat berada dimasa lalu.
S + would + bare infinitive
He would forgive you. (Dia akan memaafkanmu.)
N. PAST FUTURE CONTINOUS TENSE
Past future continuous tense adalah suatu bentuk kata kerja untuk menyatakan aksi atau situasi imajiner yang sedang berlangsung apabila unreal condition-nya terpenuhi (present continuous conditional ~ conditional sentence type 2 dengan continuous tense).
Rumus:
S + would + be + present participle
I would be attending the conference if I was in Jakarta. (Saya akan sedang menghadiri konferensi tersebut jika saya ada di Jakarta.)
Fakta:
but I’m not in Jakarta (tapi saya tidak di Jakarta)
O. PAST FUTURE PERFECT TENSE
Past future perfect tense digunakan untuk membicarakan suatu aksi yang tidak terjadi di masa lalu (conditional sentence type 3).
Rumus:
S + would + have + past participle/V-3
If you had saved your jewelry and foreign currency in a safety deposit box, they wouldn’t have gone.
(Jika kamu telah menyimpan perhiasan dan mata uang asingmu di safety deposit box, mereka tidak akan hilang.)
P. PAST FUTURE PERFECT CONTINOUS TENSE
Past future perfect continuous tense adalah suatu bentuk kata kerja untuk menyatakan suatu aksi atau situasi imajiner sedang berlangsung pada titik tertentu atau selama periode tertentu di masa lampau (perfect continuous conditional ~ conditional type 3 dengan continuous)
Rumus:
S + would + have + been + present participle
If his Visa had been approved, he would have been working abroad for a week.
(Jika visa dia telah disetujui, dia akan telah bekerja selama seminggu.)
Fakta:
but his Visa wasn’t approved (tapi Visa-nya tidak disetujui)
B. Berdasarkan Kata Kerja (Verbal dan nominal)
Dilihat dari kata kerjanya, terdapat dua jenis kata kalimat bahasa Inggris:
1. Verbal
Kalimat verbal yaitu kalimat yang terdapat kata kerjanya (verb)
Contoh:
- Tifany goes to school
- Smith is watching TV now
2. Nominal
Kalimat nominal yaitu kalimat yang tidak terdapat kata kerja, tetapi menggunakan to be. Ada beberapa bentuk to be sesuai dengan tenses-nya, karena dibelakang predikat terdapat kata benda, sifat atau keterangan yang mengacu pada subyek.
a. Simple Present → is, am, are.
Contoh :
- I am a student.
- The cakes are delicious.
b. Simple Past → was,were
Contoh :
- My neighbor was a criminal .
- The rooms were very dirty yesterday
c. Simple Future → will be
Contoh :
Contoh :
- My father will be there soon.
- Tiffany will be a teacher.
c. Perfect → has been, have been, had been
Contoh :
Contoh :
- My father has been a single parent for 16 years.
- The house has been empty since 1990.


Sangat lengkap penjelasannya kak, mempermudah saya yang sedang belajar bahasa Inggris, terimakasih.
ReplyDelete